India’s push for a greener future intensifies as 3 Govt Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) raise ethanol prices, targeting ESY 2023-24.
The 3 PSU’s – Indian Oil Corporation (IOC), Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Ltd (HPCL), and Bharat Petroleum Corporation Ltd (BPCL) – have raised the price they pay for ethanol made from a specific type of molasses by Rs 6.87 per liter.
The change applies to the ethanol supply year 2023-24, which began last month. It should be noted that this increase is the largest in over 5 years.
C molasses, a byproduct of sugar factories, is being utilized for ethanol production, promoting a #GreenEconomy,” stated the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas in a tweet on Friday.
The current procurement price for ethanol derived from C-heavy molasses is Rs 56.28 per liter.
- The buying cost of ethanol obtained from C-heavy molasses was Rs 49.41 per liter in the previous Ethanol Supply Year (ESY) 2022-23.
- With the recent increase, the new procurement price is set at Rs 56.28 per liter.
- This price rise follows the government’s decision to halt the production of ethanol from sugarcane juice by sugar mills for the 2023-24 period, citing concerns about India’s sugar production during that year.
Presently, ethanol prices are as follows: Rs 64 per litre from damaged rice, Rs 66.07 from maize, Rs 56.28 per litre from C-heavy molasses, and Rs 60.73 per litre from B-heavy molasses.

Ethanol Supply Year (ESY), C-heavy molasses contributed to 1% in 2022-23
- During the Ethanol Supply Year (ESY) 2022-23, Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) initiated a tender process for the procurement of 599.7 crore liters of ethanol. Letters of Intent (LoIs) were issued for 567 crore liters.
- Among the sources, sugarcane juice contributed 25% to total ethanol production, B-heavy molasses accounted for 45%, C-heavy molasses constituted 1%, and foodgrains made up 29%.
- For the upcoming period, OMCs are anticipated to procure 5.62 billion liters of ethanol.
- About 47.86% of this is expected to come from B and C-heavy molasses, with the remaining portion sourced from grains.
- India’s sugar production for the Ethanol Supply Year 2023-24 is projected to be around 29 million tonnes, a decline from the 33 million tonnes produced in ESY 2022-23.
Indian Sugar Mills Association Applauds The Move

- M Prabhakar Rao, President of ISMA (Indian Sugar Mills Association), compliments for the Rs. 6.87 per litre incentive on ethanol from C Heavy Molasses, bringing the price to Rs. 56.28 per litre.
- However, he suggested a further increase to assist the industry in navigating uncertainties, ensuring timely cane price payments, mitigating losses, and boosting ethanol production.
- Rao highlighted the industry’s challenge of paying high interest on investments in increased ethanol production capacity, which is not being fully utilized.
- Furthermore, he reiterated the industry’s appeal for an immediate ban on molasses export and emphasized the anticipation of a further price increase for ethanol derived from B-heavy molasses and sugarcane juice.
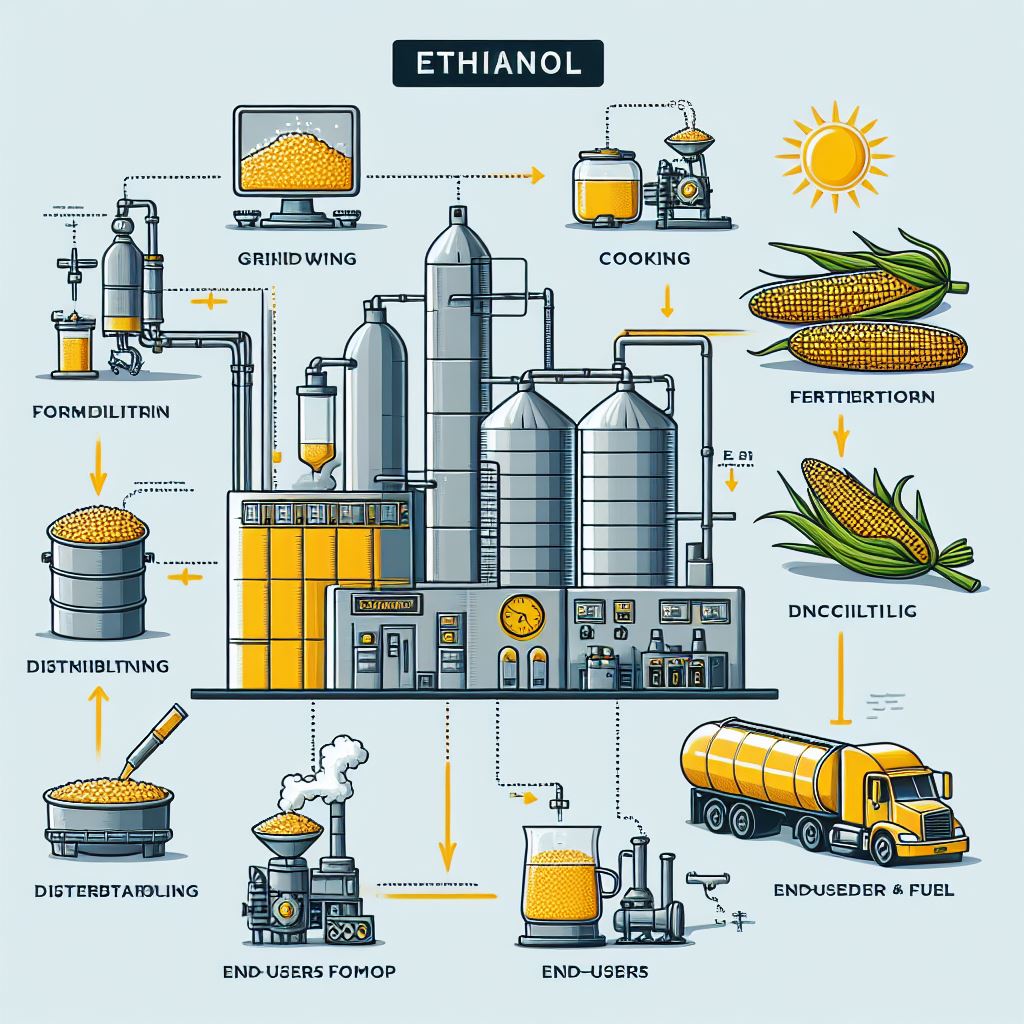
OMCs targeting 15% ethanol blending in 2023-24
- As per the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Oil Marketing Companies (OMCs) successfully achieved a 12 per cent ethanol blending rate in the Ethanol Supply Year (ESY) 2022-23, which marked an increase from the 10 per cent achieved in ESY 2021-22.
- Looking ahead to ESY 2023-24, these oil retailers are setting a target to achieve a 15 per cent ethanol blending rate.
- This indicates a continued effort to enhance the ethanol blending ratio, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly fuel mix.
Why Government Is Encouraging Ethanol Production?
The government is encouraging ethanol production for several reasons:
1. Environmental Benefits:
Ethanol is considered a cleaner and more environmentally friendly fuel compared to traditional fossil fuels.
Its combustion produces fewer greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce air pollution.
2. Reduced Dependence on Fossil Fuels:
Promoting ethanol production helps reduce the country’s reliance on traditional fossil fuels like petrol.
This diversification of the energy mix enhances energy security by providing an alternative and renewable source of fuel.
3. Agricultural Utilization:
Ethanol is often produced from agricultural crops or byproducts, providing an additional market for farmers.
This can contribute to the rural economy by creating new income streams and employment opportunities in the agricultural sector.
4. Energy Independence:
Encouraging the production of ethanol supports efforts to achieve energy independence by utilizing domestic resources.
This is particularly important for countries looking to reduce dependence on imported oil and enhance their energy self-sufficiency.
5. Compliance with Regulations:
Many governments worldwide are implementing regulations to increase the percentage of ethanol blended with petrol.
Encouraging ethanol production helps meet these regulatory requirements, promoting the use of cleaner fuels in the transportation sector.
6. Economic Benefits:
The ethanol industry can stimulate economic growth by creating jobs in production, distribution, and related sectors.
Additionally, it can attract investment in research and development for more efficient and sustainable ethanol production methods.
7. Waste Utilization:
Ethanol can be produced from various feedstocks, including agricultural residues and byproducts.
This promotes the efficient use of resources and reduces waste, aligning with principles of circular economy and sustainable resource management.
8. Energy Security:
Diversifying the energy mix with ethanol contributes to energy security by reducing vulnerability to price fluctuations in global oil markets. It provides a stable and locally sourced alternative fuel supply.
In summary, the government’s encouragement of ethanol production aligns with broader goals related to environmental sustainability, economic development, energy security, and compliance with regulatory frameworks promoting cleaner fuels.








